| 12.2.40 make-random-state | Function |
- Syntax:
-
make-random-state
&optional state
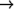 new-state
new-state
- Arguments and Values:
-
state - a random state, or nil, or t.
The default is nil.
new-state - a random state object.
- Description:
-
Creates a fresh object of type random-state suitable
for use as the value of *random-state*.
If state is a random state object, the new-state is a copy5 of that object. If state is nil, the new-state is a copy5 of the current random state. If state is t, the new-state is a fresh random state object that has been randomly initialized by some means.
- Examples:
-
(let* ((rs1 (make-random-state nil)) (rs2 (make-random-state t)) (rs3 (make-random-state rs2)) (rs4 nil)) (list (loop for i from 1 to 10 collect (random 100) when (= i 5) do (setq rs4 (make-random-state))) (loop for i from 1 to 10 collect (random 100 rs1)) (loop for i from 1 to 10 collect (random 100 rs2)) (loop for i from 1 to 10 collect (random 100 rs3)) (loop for i from 1 to 10 collect (random 100 rs4))))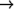 ((29 25 72 57 55 68 24 35 54 65)
(29 25 72 57 55 68 24 35 54 65)
(93 85 53 99 58 62 2 23 23 59)
(93 85 53 99 58 62 2 23 23 59)
(68 24 35 54 65 54 55 50 59 49))
((29 25 72 57 55 68 24 35 54 65)
(29 25 72 57 55 68 24 35 54 65)
(93 85 53 99 58 62 2 23 23 59)
(93 85 53 99 58 62 2 23 23 59)
(68 24 35 54 65 54 55 50 59 49))
- Exceptional Situations:
-
Should signal an error of type type-error if state is not a random state, or nil, or t.
- See Also:
-
random, *random-state*
- Notes:
-
One important use of make-random-state is to allow the same
series of pseudo-random numbers to be generated many times within a
single program.
- Allegro CL Implementation Details:
- See cl:random and cl:make-random-state for information on the Allegro CL implementation of make-random-state.