| 12.2.38 sqrt, isqrt | Function |
- Syntax:
-
sqrt
number
 root
root
isqrt natural
 natural-root
natural-root
- Arguments and Values:
-
number, root - a number.
natural, natural-root - a non-negative integer.
- Description:
-
sqrt and isqrt compute square roots.
sqrt returns the principal square root of number. If the number is not a complex but is negative, then the result is a complex.
isqrt returns the greatest integer less than or equal to the exact positive square root of natural.
If number is a positive rational, it is implementation-dependent whether root is a rational or a float. If number is a negative rational, it is implementation-dependent whether root is a complex rational or a complex float.
The mathematical definition of complex square root (whether or not minus zero is supported) follows:
(sqrt x) = (exp (/ (log x) 2))
The branch cut for square root lies along the negative real axis, continuous with quadrant II. The range consists of the right half-plane, including the non-negative imaginary axis and excluding the negative imaginary axis.
- Examples:
-
(sqrt 9.0)
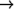 3.0
(sqrt -9.0)
3.0
(sqrt -9.0) 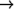 #C(0.0 3.0)
(isqrt 9)
#C(0.0 3.0)
(isqrt 9) 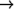 3
(sqrt 12)
3
(sqrt 12) 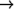 3.4641016
(isqrt 12)
3.4641016
(isqrt 12) 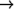 3
(isqrt 300)
3
(isqrt 300) 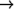 17
(isqrt 325)
17
(isqrt 325)  18
(sqrt 25)
18
(sqrt 25)
 5
OR
5
OR 5.0
(isqrt 25)
5.0
(isqrt 25)  5
(sqrt -1)
5
(sqrt -1)  #C(0.0 1.0)
(sqrt #c(0 2))
#C(0.0 1.0)
(sqrt #c(0 2))  #C(1.0 1.0)
#C(1.0 1.0)
- Exceptional Situations:
-
The function sqrt should signal type-error if its argument
is not a number.
The function isqrt should signal type-error if its argument is not a non-negative integer.
The functions sqrt and isqrt might signal arithmetic-error.
- See Also:
-
exp,
log,
Section 12.1.3.3 Rule of Float Substitutability
- Notes:
-
(isqrt x) ==(values (floor (sqrt x)))
but it is potentially more efficient. - Allegro CL Implementation Details:
- None.