| 12.2.69 ldb | Accessor |
- Syntax:
-
ldb
bytespec integer
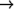 byte
byte
(setf (ldb bytespec place) new-byte)
- Pronunciation:
-
[ 'lidib ]
or [ 'lidEb ]
or [ 'el'dê'bê ]
- Arguments and Values:
-
bytespec - a byte specifier.
integer - an integer.
byte, new-byte - a non-negative integer.
- Description:
-
ldb extracts and returns the byte of integer
specified by bytespec.
ldb returns an integer in which the bits with weights 2(s-1) through 20 are the same as those in integer with weights 2(p+s-1) through 2p, and all other bits zero; s is (byte-size bytespec) and p is (byte-position bytespec).
setf may be used with ldb to modify a byte within the integer that is stored in a given place. The order of evaluation, when an ldb form is supplied to setf, is exactly left-to-right. The effect is to perform a dpb operation and then store the result back into the place.
- Examples:
-
(ldb (byte 2 1) 10)
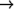 1
(setq a (list 8))
1
(setq a (list 8)) 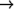 (8)
(setf (ldb (byte 2 1) (car a)) 1)
(8)
(setf (ldb (byte 2 1) (car a)) 1) 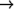 1
a
1
a 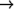 (10)
(10)
- See Also:
-
byte,
byte-position,
byte-size,
dpb
- Notes:
-
(logbitp j (ldb (byte s p) n)) ==(and (< j s) (logbitp (+ j p) n))In general,
(ldb (byte 0 x) y)
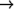 0
0
for all valid values of x and y.
Historically, the name "ldb" comes from a DEC PDP-10 assembly language instruction meaning "load byte."
- Allegro CL Implementation Details:
- None.