- Syntax:
- defgeneric function-name gf-lambda-list [[
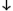 option | {method-description}*]]
option | {method-description}*]]
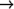 new-generic
new-generic option::= (:argument-precedence-order {parameter-name}+)
|
(declare {gf-declaration}+) |
(:documentation gf-documentation) |
(:method-combination method-combination {method-combination-argument}*)
|
(:generic-function-class generic-function-class) |
(:method-class method-class)
(method-description::= :method {method-qualifier}* specialized-lambda-list
[[{declaration}* | documentation]] {form}*)
- Arguments and Values:
- function-name - a function name.
generic-function-class - a non-nil
symbol naming a class.
gf-declaration - an optimize declaration specifier; other declaration specifiers are not
permitted.
gf-documentation - a string;
not evaluated.
gf-lambda-list - a generic function lambda list.
method-class - a non-nil symbol naming a class.
method-combination-argument - an object.
method-combination-name - a symbol
naming a method combination type.
method-qualifiers, specialized-lambda-list, declarations, documentation,
forms - as per defmethod.
new-generic - the generic
function object.
parameter-name - a symbol
that names a required parameter
in the lambda-list. (If the :argument-precedence-order option is
specified, each required parameter
in the lambda-list must be used exactly once as a parameter-name.)
- Description:
- The macro defgeneric is used to define a generic function or to specify options
and declarations that pertain to a generic
function as a whole.
If function-name is a list it must be of the form (setf symbol).
If (fboundp function-name) is false,
a new generic function is created.
If (fdefinition function-name) is a generic function, that generic function is modified. If function-name
names an ordinary function, a macro, or a special operator, an error is signaled.
The effect of the defgeneric
macro is as if the following three steps were performed: first, methods defined by previous defgeneric forms
are removed; second, ensure-generic-function is called;
and finally, methods specified by the
current defgeneric form are added to the generic function.
Each method-description defines a method
on the generic function. The lambda list of each method must be congruent with the lambda list specified by the gf-lambda-list
option. If no method descriptions are
specified and a generic function of
the same name does not already exist, a generic
function with no methods is created.
The gf-lambda-list argument of defgeneric
specifies the shape of lambda lists for
the methods on this generic function. All methods on the resulting generic function must have lambda lists that are congruent with this
shape. If a defgeneric form is evaluated
and some methods for that generic function have lambda lists that are not congruent with that
given in the defgeneric form, an error is
signaled. For further details on method congruence, see Section 7.6.4 Congruent Lambda-lists for all Methods of a Generic
Function.
The generic function
passes to the method all the argument values
passed to it, and only those; default values are not supported. Note that optional and
keyword arguments in method definitions, however, can have default initial value forms and
can use supplied-p parameters.
The following options are provided. Except as otherwise noted, a given option
may occur only once.
- The :argument-precedence-order option is used to specify the order in
which the required arguments in a call to the generic function are tested for
specificity when selecting a particular method.
Each required argument, as specified in the gf-lambda-list argument, must be
included exactly once as a parameter-name so that the full and unambiguous
precedence order is supplied. If this condition is not met, an error is signaled.
- The declare option is used to specify
declarations that pertain to the generic
function.
An optimize declaration specifier is allowed. It
specifies whether method selection should be optimized for speed or space, but it has no
effect on methods. To control how a method is optimized, an optimize
declaration must be placed directly in the defmethod form or method description. The optimization
qualities speed and space are the only qualities this standard requires, but
an implementation can extend the object system to recognize other qualities. A simple
implementation that has only one method selection technique and ignores optimize declaration specifiers is valid.
The special, ftype,
function, inline, notinline, and declaration
declarations are not permitted. Individual implementations can extend the declare option to support additional declarations. If an
implementation notices a declaration
specifier that it does not support and that has not been proclaimed as a
non-standard declaration identifier
name in a declaration proclamation, it should issue a warning.
The declare option may be specified more than
once. The effect is the same as if the lists of declaration specifiers had been
appended together into a single list and specified as a single declare
option.
- The :documentation argument is a documentation string to be attached
to the generic function object, and to be attached with kind function to the function-name.
- The :generic-function-class option may be used to specify that the generic function is to have a different class than the default provided by the system (the class standard-generic-function).
The class-name argument is the name of a class
that can be the class of a generic function. If function-name
specifies an existing generic function
that has a different value for the :generic-function-class argument and the new
generic function class is compatible with the
old, change-class is called to change the class of the generic function; otherwise an error is
signaled.
- The :method-class option is used to specify that all methods on this generic function are to have a different class from the default provided by the system (the class standard-method).
The class-name argument is the name of a class
that is capable of being the class of a method.
- The :method-combination option is followed by a symbol that names a
type of method combination. The arguments (if any) that follow that symbol depend on the
type of method combination. Note that the standard method combination type does not
support any arguments. However, all types of method combination defined by the short form
of define-method-combination accept an optional argument
named order, defaulting to :most-specific-first, where a value of :most-specific-last
reverses the order of the primary methods
without affecting the order of the auxiliary methods.
The method-description arguments define methods that will be associated with the generic function. The method-qualifier
and specialized-lambda-list arguments in a method description are the same as for defmethod.
The form arguments specify the method body. The body of the method is enclosed in an implicit block. If function-name is
a symbol, this block bears the same name as
the generic function. If function-name
is a list of the form (setf symbol),
the name of the block is symbol.
Implementations can extend defgeneric
to include other options. It is required that an implementation signal an error if it
observes an option that is not implemented locally.
defgeneric is not required to
perform any compile-time side effects. In particular, the methods are not installed for invocation during
compilation. An implementation may
choose to store information about the generic
function for the purposes of compile-time error-checking (such as checking the
number of arguments on calls, or noting that a definition for the function name has been
seen).
- Examples:
-
- Exceptional Situations:
- If function-name names an ordinary
function, a macro, or a special operator, an error of type program-error
is signaled.
Each required argument, as specified in the gf-lambda-list
argument, must be included exactly once as a parameter-name, or an error of type program-error
is signaled.
The lambda list of each method specified by a method-description
must be congruent with the lambda list
specified by the gf-lambda-list option, or an error of type error is
signaled.
If a defgeneric form is
evaluated and some methods for that generic function have lambda lists that are not congruent with that
given in the defgeneric form, an error of type error is
signaled.
A given option may occur only once, or an error of type program-error
is signaled.
If function-name specifies an existing generic function that has a different
value for the :generic-function-class argument and the new generic function class is compatible with the old, change-class is called to change the class of the generic function; otherwise an error of type error is
signaled.
Implementations can extend defgeneric
to include other options. It is required that an implementation signal an error of type program-error
if it observes an option that is not implemented locally.
- See Also:
- defmethod, documentation,
ensure-generic-function, generic-function,
Section 7.6.4 Congruent Lambda-lists for all Methods of
a Generic Function
- Allegro CL Implementation Details:
- None.
![]()
![]()